TOASTED LEMON QUINOA CABBAGE SALAD
5th June 2019BAKED PINEAPPLE SALMON
11th July 2019Seo Tips for Beginners
SEO TIPS FOR BEGINNERS
For the uninitiated, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) might sound a little sleazy. If you need to use special techniques to help your site appear at the top of Google search results, doesn’t that mean that — in some weird way — you’re cheating?
At the end of the day, Google needs to consider a variety of factors in order to help internet users find the most relevant websites for their search queries. Don’t think of SEO as a cheat code, think of it as a search engine aid. After all, when you’re typing things like “what in the world is SEO” into your Google search bar, articles that tell you just that are exactly what you want to find, right?
Choose Your Hosting Provider Carefully
We’re not just saying this because we’re a hosting company. We’re saying it because it’s true: the hosting provider you pick is vital for SEO.
Pick a Theme That’s Optimized for Search Engines
Your theme is one of the most important choices you’ll make for your WordPress site. It determines your site’s appearance and layout, can provide new functionality, and also plays a role in its SEO.
Use a Dedicated SEO Plugin
There are many plugins designed specifically to improve your site’s SEO.
Change Your ‘Permalink’ Structure
Permalinks are the permanent URLs that point to your site’s individual posts, pages, and other content. They’re what people will use to reference and link back to your site, and their appearance matters. Clear, descriptive links that describe their content are easier for search engines to make sense of and tend to get a ranking boost.WordPress offers a number of automatic permalink options:
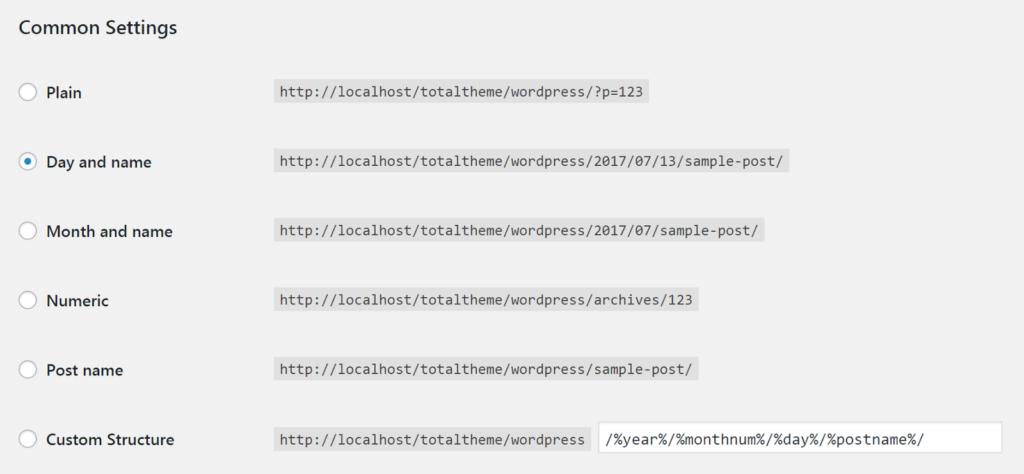
A few are based around numbers (such as the Plainand Numericoptions), which isn’t ideal since they convey little useful information to search engines. Instead, you’re best off with the Post Namestructure since it communicates clearly what the linked content is about. You can easily change your permalink structure (or create a custom one) by visiting your site’s back end and navigating to Settings > Permalink.
Find and Use Relevant Keywords
You can identify popular search terms and phrasing usingGoogle Keyword Planner. What Google Keyword Planner does is take people’s search prompts and assign value to each of them.
Simply log in with your Google account and select “Search for new keywords using a phrase, website, or category.” Type something in — say, “risotto recipes” — and a variety of related phrases that Google users tend to search for will pop up. These phrases are called “keywords,” and they are the heart of your blog.
Use H1 Title Tags Sparingly
In HTML, H1 stands for Heading One, the largest and most prominent heading on a page. The H1 is one of the first things search engines see after the title of your page. That makes it an incredibly powerful page element.
According to SEO software company Moz’s bi-yearly survey on search engine ranking factors, the titles on your page are one of the nine most important considerations a search engine makes.
It’s easy to add multiple H1 headings to a page, by simply surrounding text with <h1></h1> tags. But doing so can confuse search engines, who will prioritize an H1 heading if there is only one, but treat them as less relevant content if they’re used a lot.
Use an H1 for the biggest heading on your page, and H2 or H3 headings for subheads or section heads.
As for what should be in that H1 title? Something relevant to searchers. You know, like a keyword.
Create a Sitemap and Tell Google About It
A sitemap is a very basic list of pages accessible to search engine “crawlers” — programs that search the web for relevant search results — and users. Sitemaps are usually written in XML, a metalanguage that crawlers can understand and transmit to search engines.
You don’t need to know any XML to write your own sitemap. You can copy Google’s example or use a variety of free, third-party tools to generate one. Or, if you’re running a WordPress site, simply install the Google XML Sitemaps plugin.
The plugin will automatically notify Google (and dozens of other search engines, for that matter) of this new crawler-friendly way for it to browse your site’s content, as will some of the third-party tools. Otherwise, you need to tell Google about it yourself. The Google Search Console Sitemaps tool will walk you through the quick process.
Incorporate Useful Internal and External Links
Google and other search engines don’t consider your website in a vacuum. Instead, they look at how well it’s connected, both internally and to other sites. Using plenty of links throughout your posts and pages tells crawlers how they relate to similar content. It also encourages other people to link back to your site — which in turn communicates to search engines that your content is valuable!
As with keywords, this is a strategy you’ll want to use carefully. If you cram too many links into your content or use a lot of links that point to irrelevant pages or exist only to promote products, your search engine rankings will likely suffer.
Instead, look to incorporate links where they fit naturally, and to point readers towards high-quality websites that already rank highly in SERPs. Smart use of both internal links and external links is key to achieving the best SEO results possible.
Use Responsive Design on Your Site
More people than ever are using mobile devices to browse the internet. This means your site needs to look and perform as good on any type of device a visitor happens to be using. You can ensure this by following the strategy of responsive design — in other words, designing your site so it reacts and adapts to each user’s device.
Optimize Your Images
Images are important for just about any website. They provide visual appeal and context, plus they help break up text and make it more readable. As you’ve probably guessed, they can also have an impact on your SEO. For one, the quality and size of your images can affect your pages’ loading speed, which is a ranking factor. Also, crawlers will look at certain information attached to images — such as filenames and ‘alt text’ — when trying to index and understand your site.
Write Long-Form Content When Possible
When Google’s algorithms are deciding how to rank content, they pay special attention to its length. That doesn’t mean shorter content never ranks highly. However, longer content has an advantage, because search engines consider it more likely to be useful. Plus, the more comprehensive your content is, the better it can communicate its topic to crawlers via keywords, headings, and so on.
Longer content is also valuable to readers, can increase your perceived credibility, and encourages visitors to spend more time on your site. So when creating content, try to make it as in-depth as possible. There are many ways to do this, but the ‘skyscraper technique’ — improving on existing content by making yours better and more comprehensive — is one method worth checking out.
Add and Update Your Posts Frequently
Along with length, Google’s algorithms consider the frequency of content when deciding how to rank your pages. Older, high-quality content will do well, of course, but a boost is given to newer, ‘fresh’ content that’s more likely to be relevant to searchers.
Therefore, if you want your site to do consistently well in SERPs over time, you’ll want to add new content regularly. Try creating a posting schedule to keep yourself on track and varying up the types of content you create to keep yourself and your visitors interested. Also, don’t neglect older posts and pages. Updating your existing content prompts crawlers to re-evaluate it and to give it higher prominence than pages that never change.
Focus on Quality Content
When Google and other search engines create complex algorithms for ranking websites, their goal is to help the most relevant and useful sites score highly.




